Embodied cognition in miniature brains and bodies of marine zooplankton
Pushing the Boundaries: Neuroscience, Cognition, and Life
June 25-27, 2023
Living Systems Institute, University of Exeter
Centre for Organismal Studies, University of Heidelberg
The ‘brain’
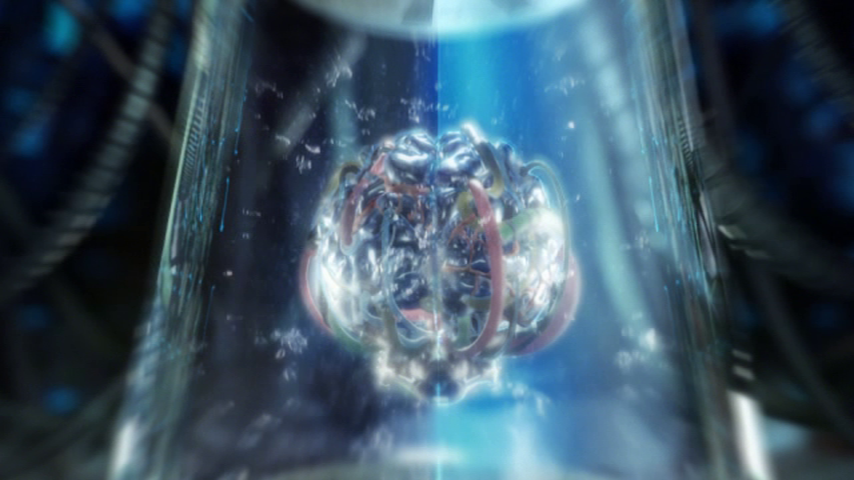

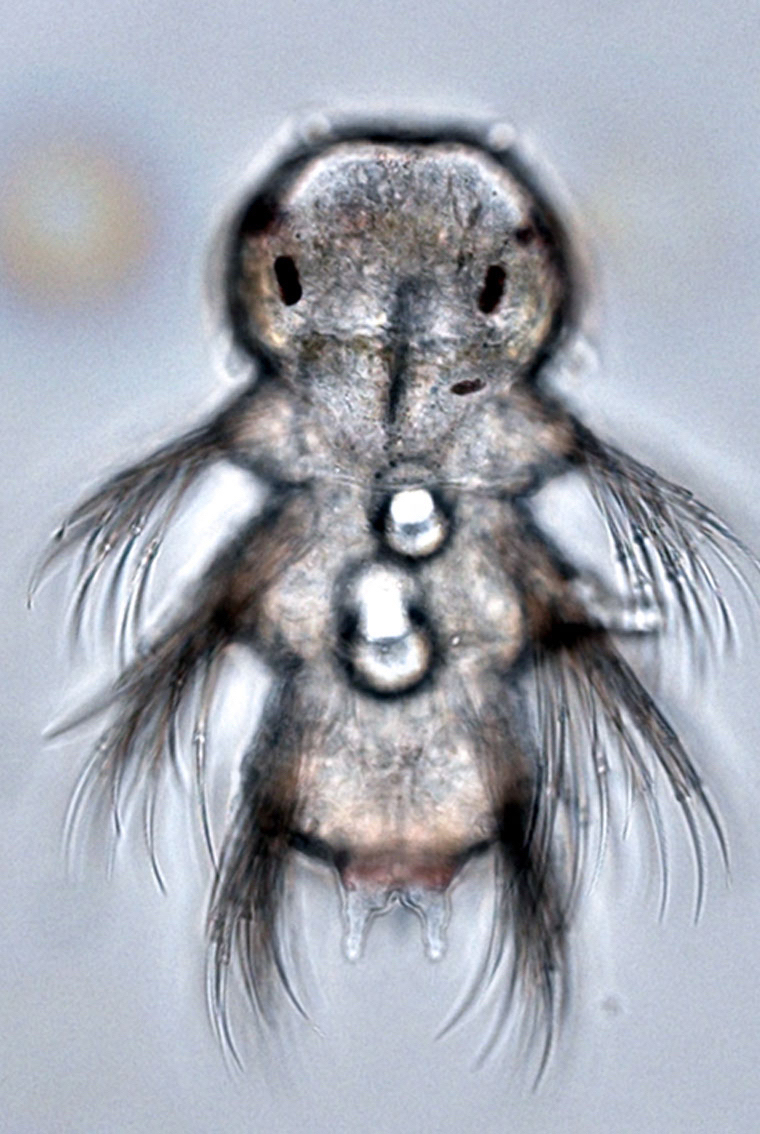
Ciliated zooplankton larvae
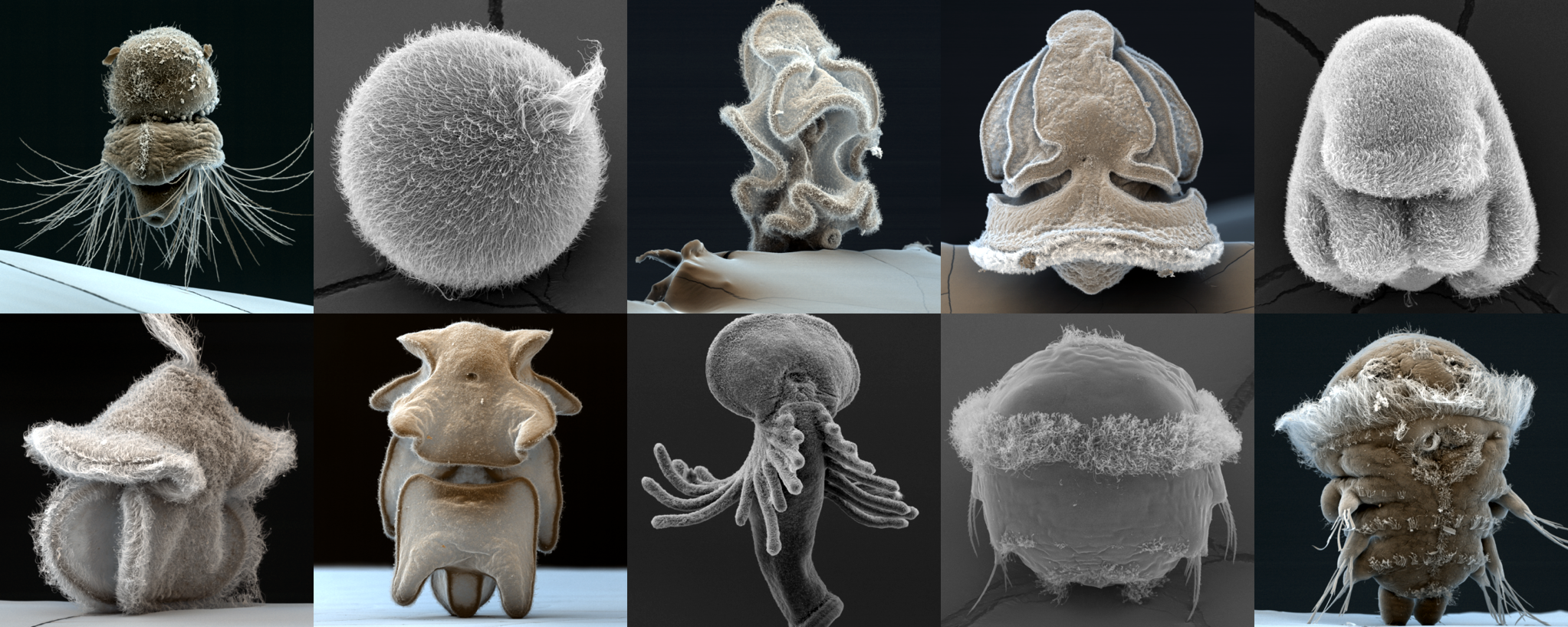
Platynereis dumerilii

- breeding culture, full life-cycle
- embryos daily, year round
- genome sequence
- microinjection, transgenesis
- neuron-specific promoters and antibodies
- knock-out lines
- neuronal connectome
- whole-body neuronal activity imaging
- whole-animal pharmacology by bath application 😎
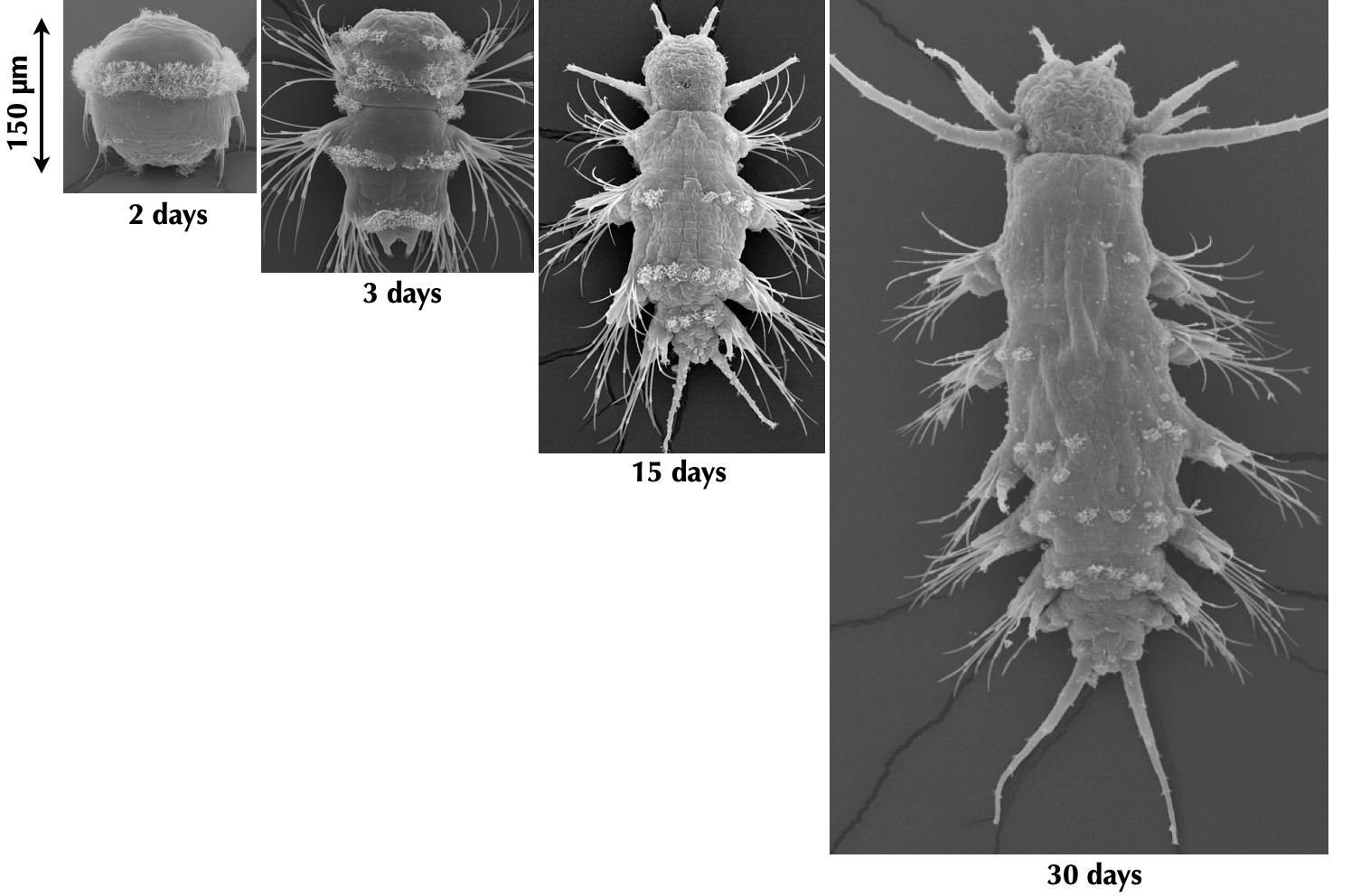
Platynereis dumerilii
Spawning
movie by Albrecht Fischer
Synchronously developing larvae
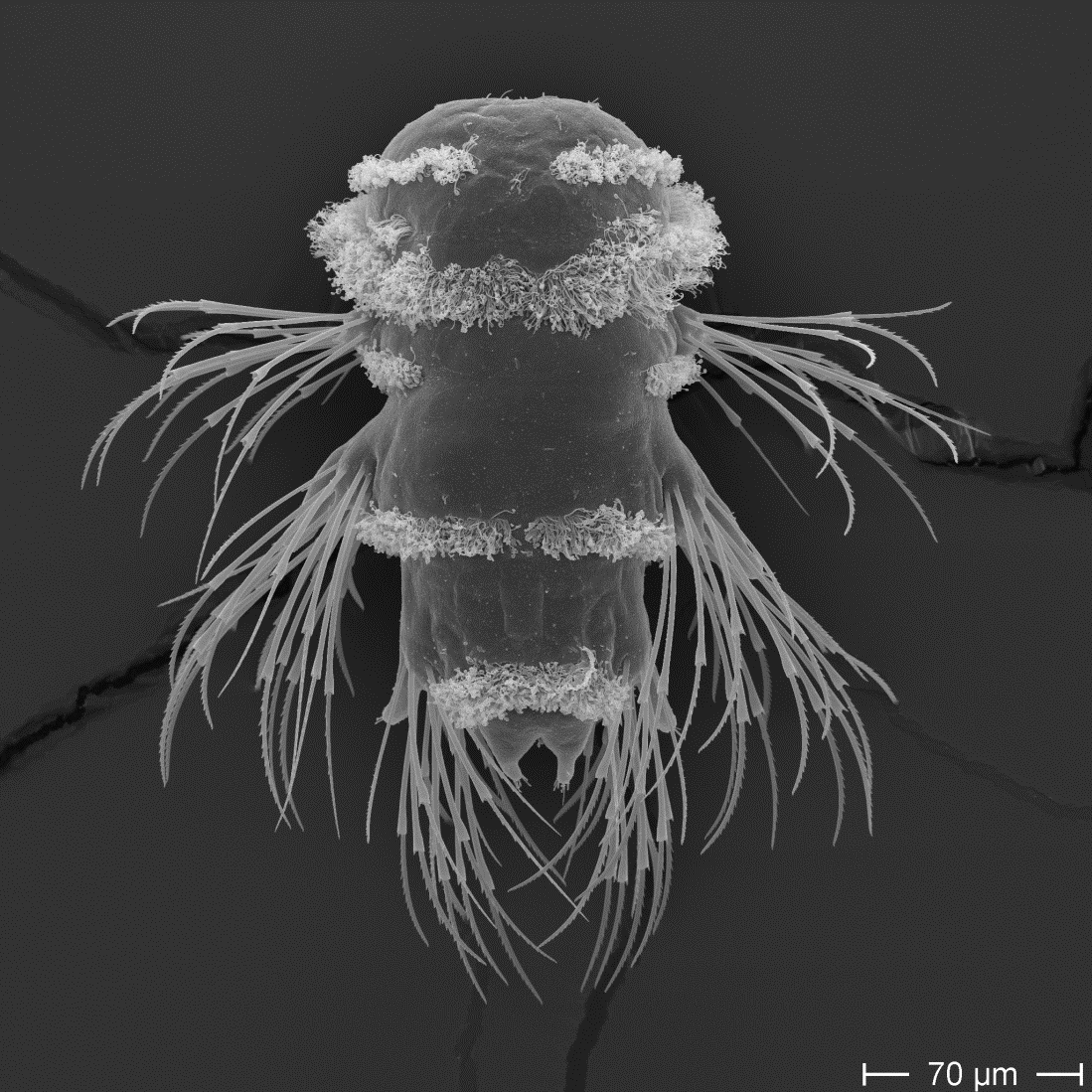
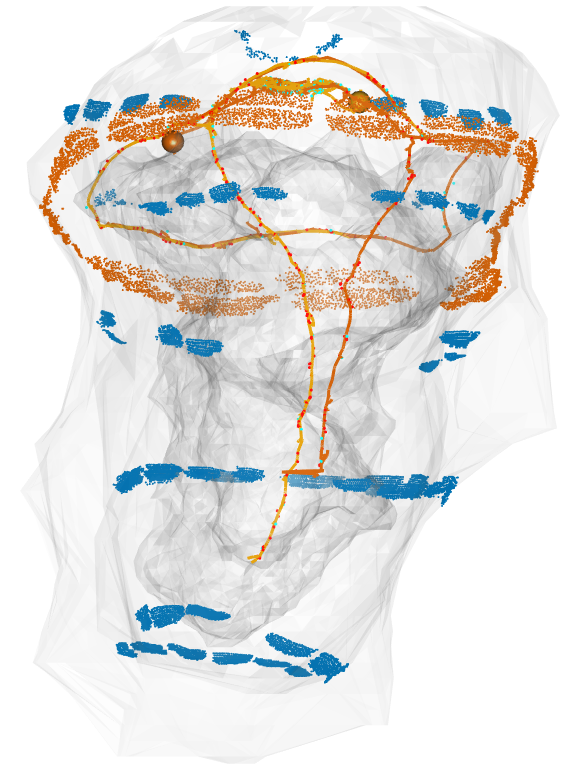
Whole-body volume EM of an entire three-day-old larva
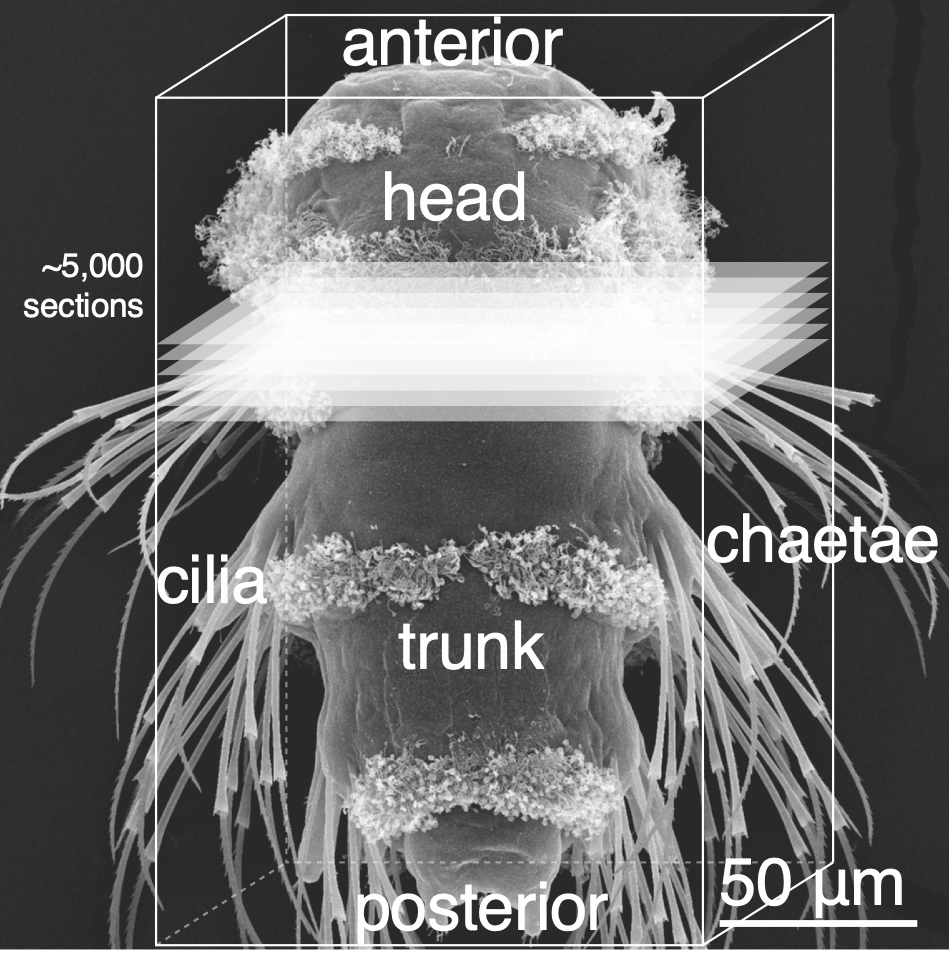
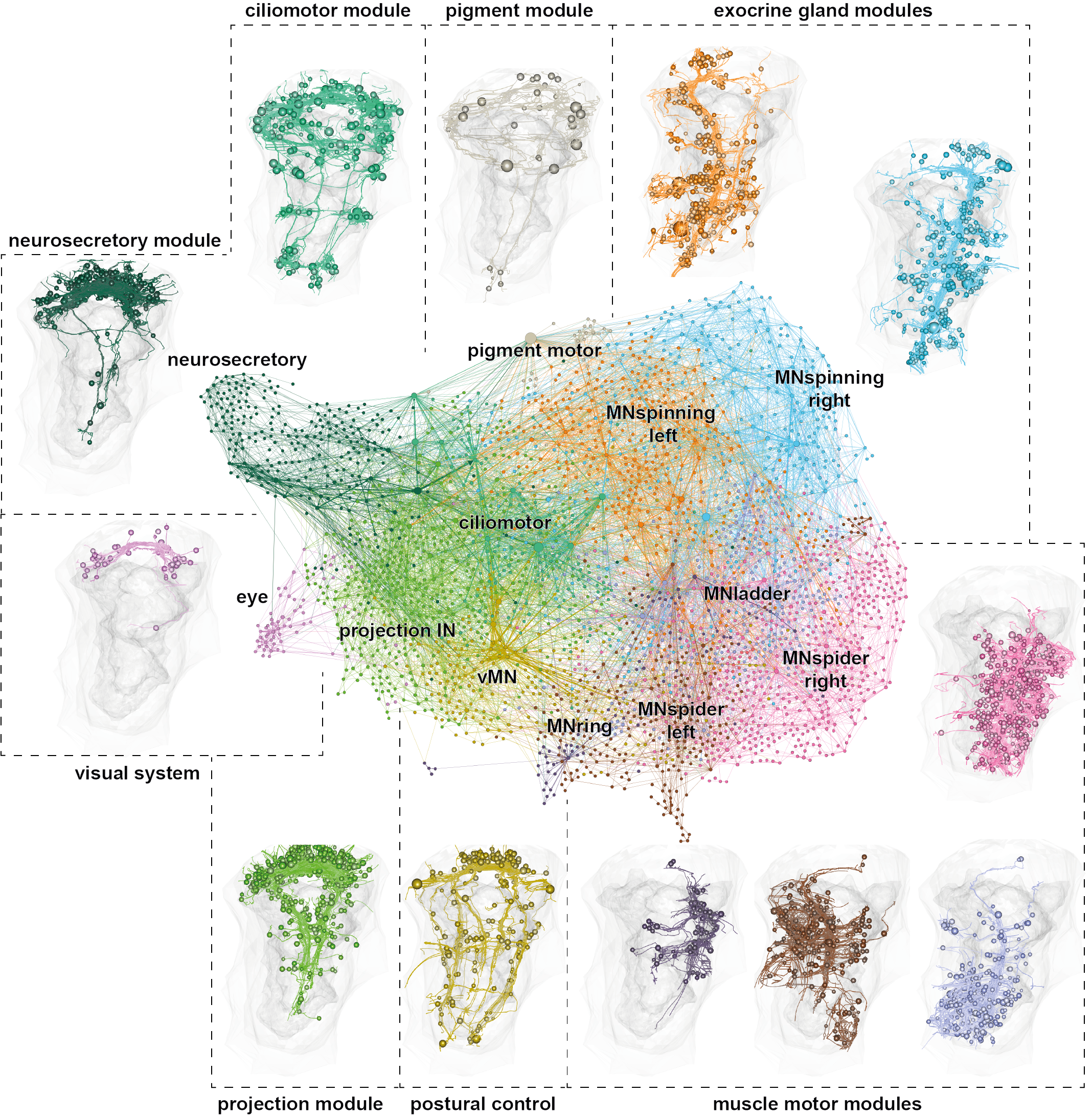
The nervous system of the larva
~2,000 neurons
Synaptic connectome
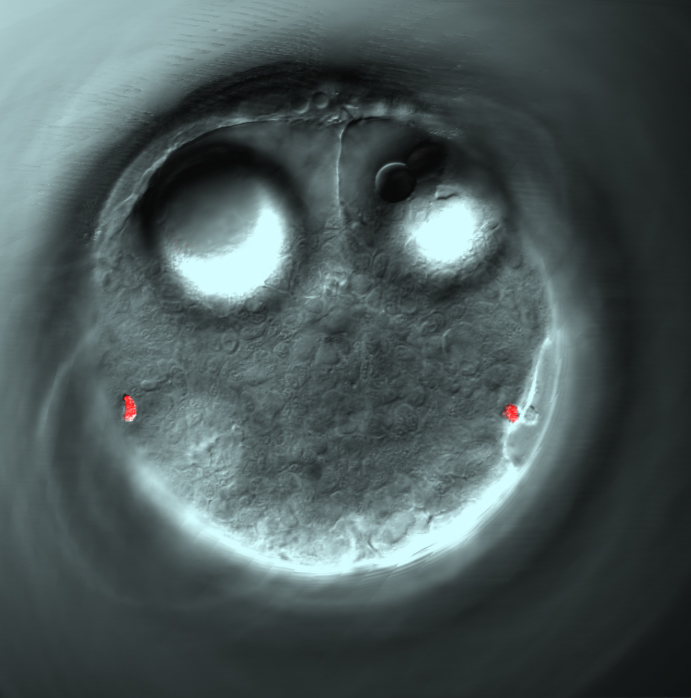
Phototaxis

Helical swimming, sensing and turning are tightly linked

Whole-body coordination of cilia

Whole-body coordination during startle
Coordinated arrest of all cilia
No arrest in polycystin receptor mutant
Copepod attack
wild type polycystin mutant 
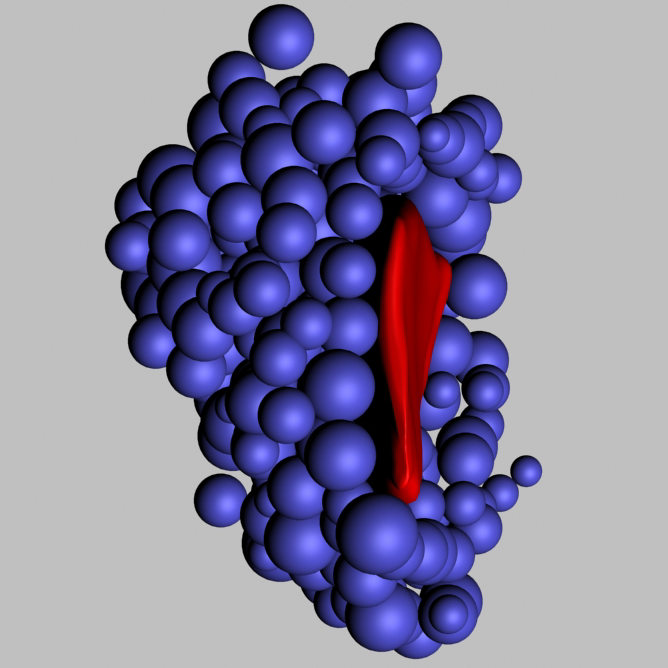
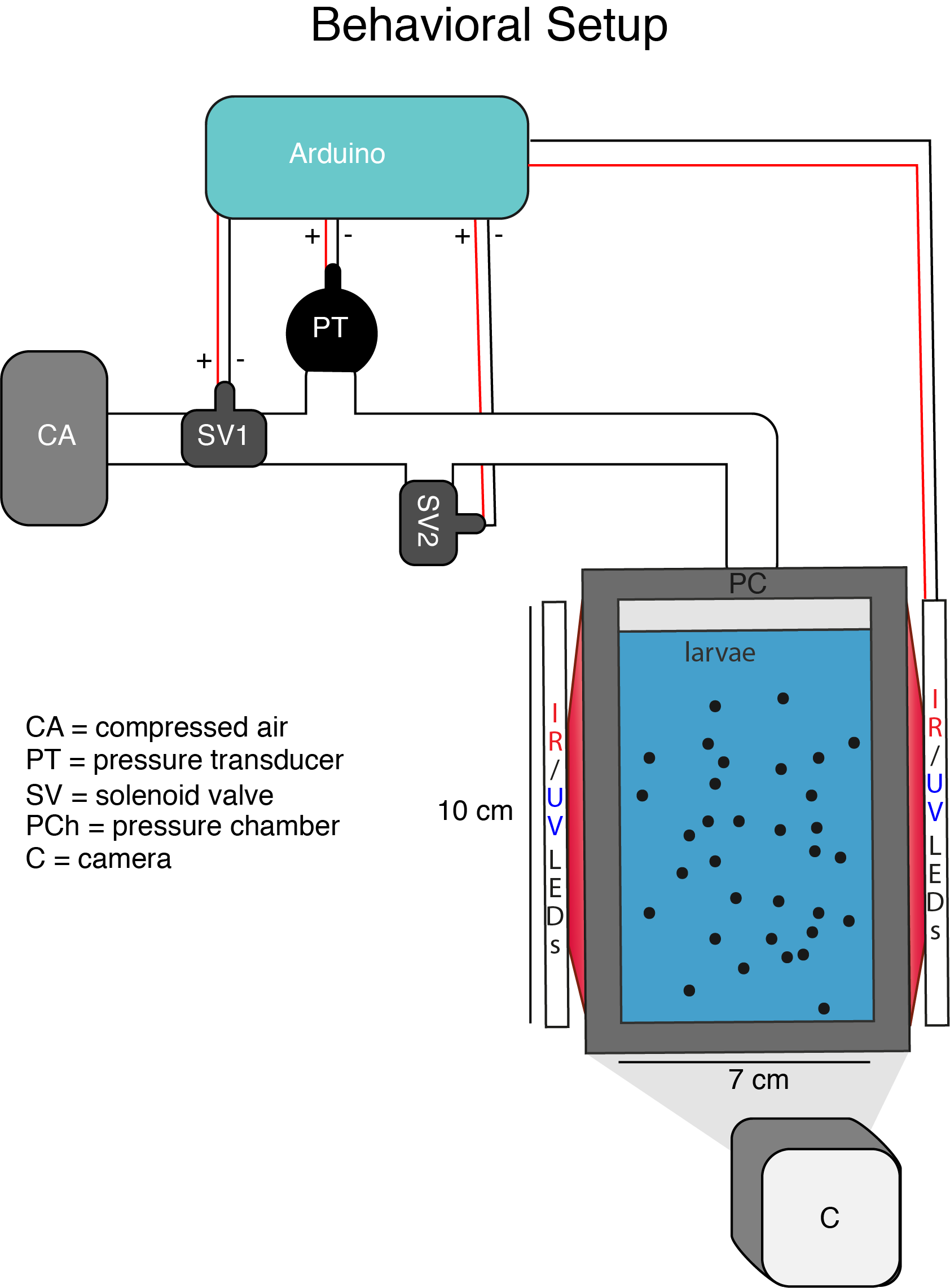
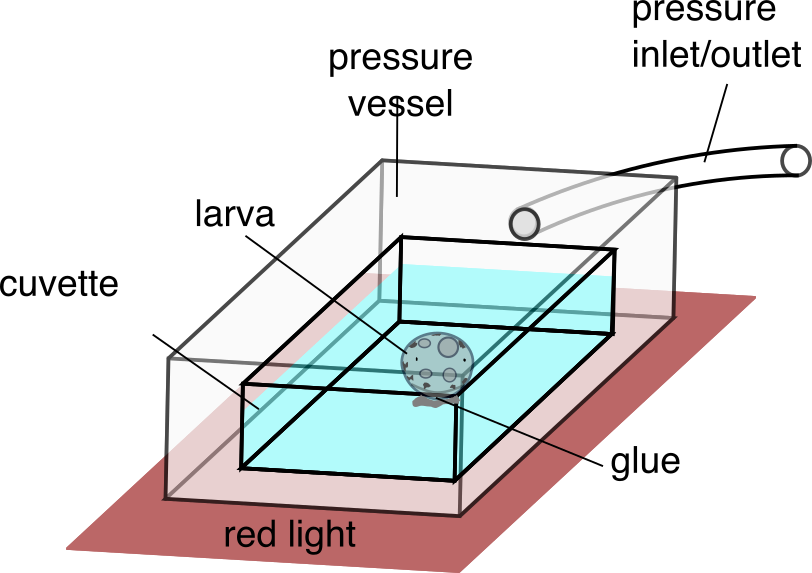
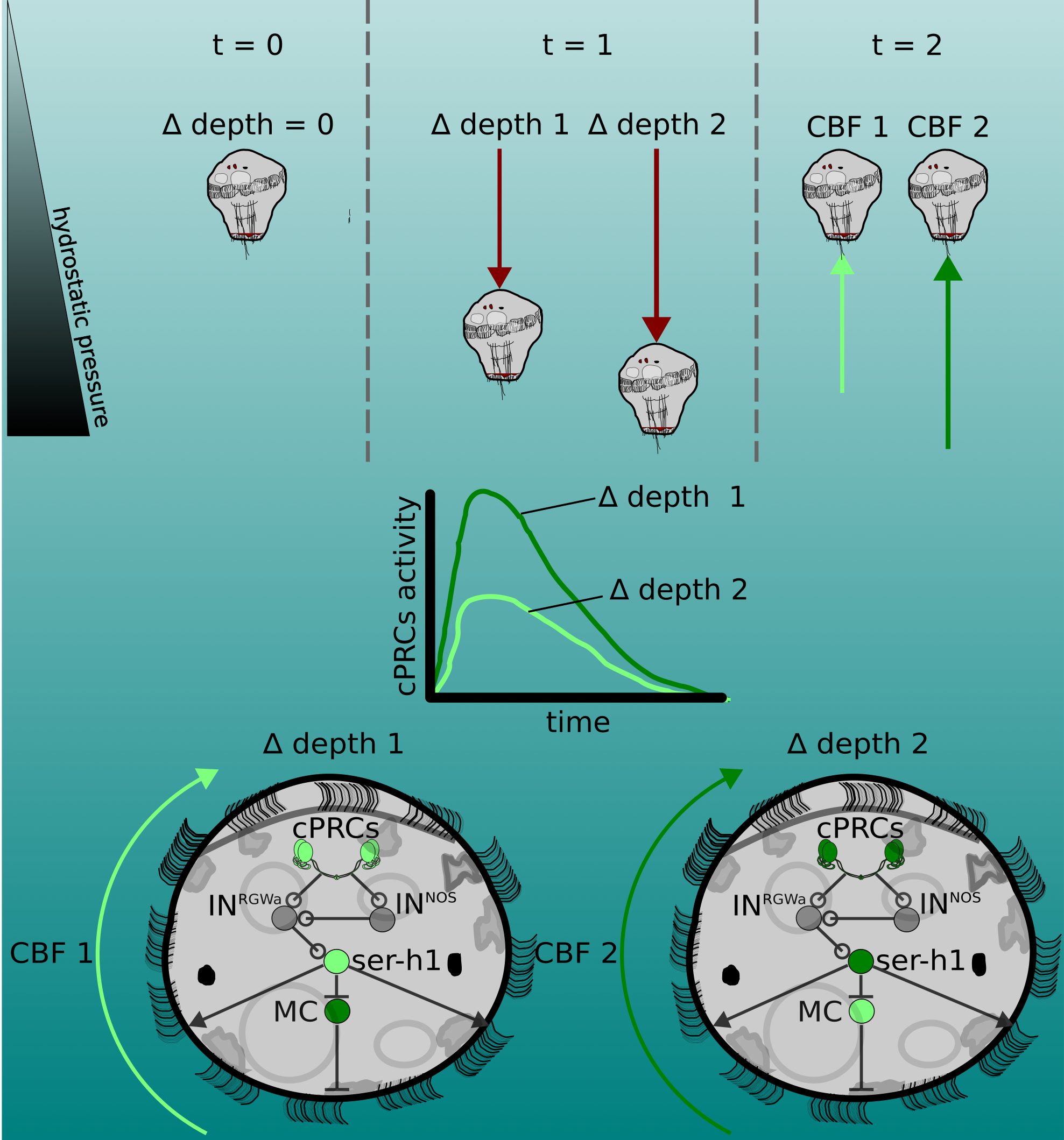
Pressure response in Platynereis larvae


Luis A. Bezares-Calderón
Precise control of pressure in the pressure chamber

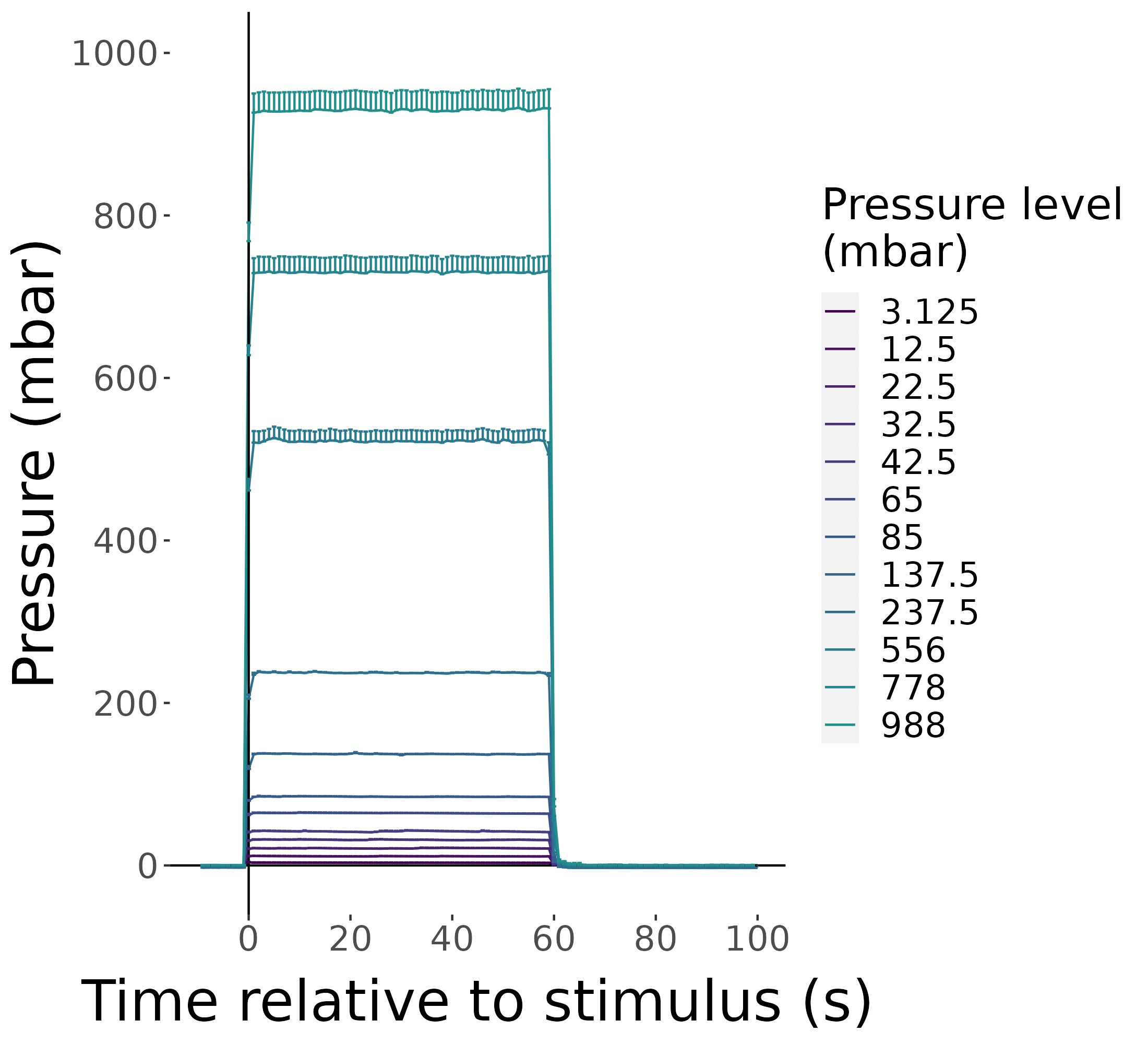
Luis A. Bezares-Calderón
Pressure response is graded
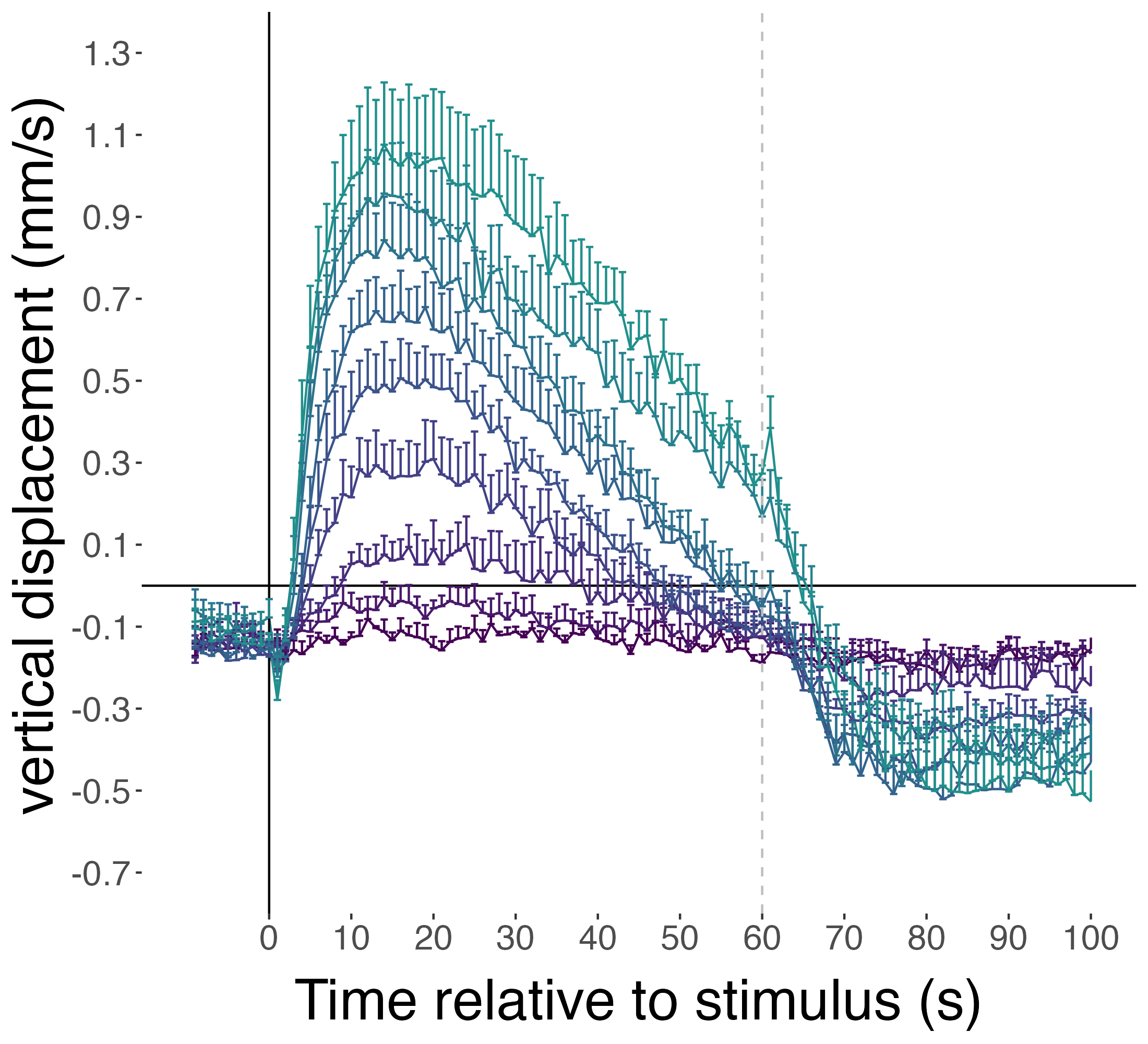
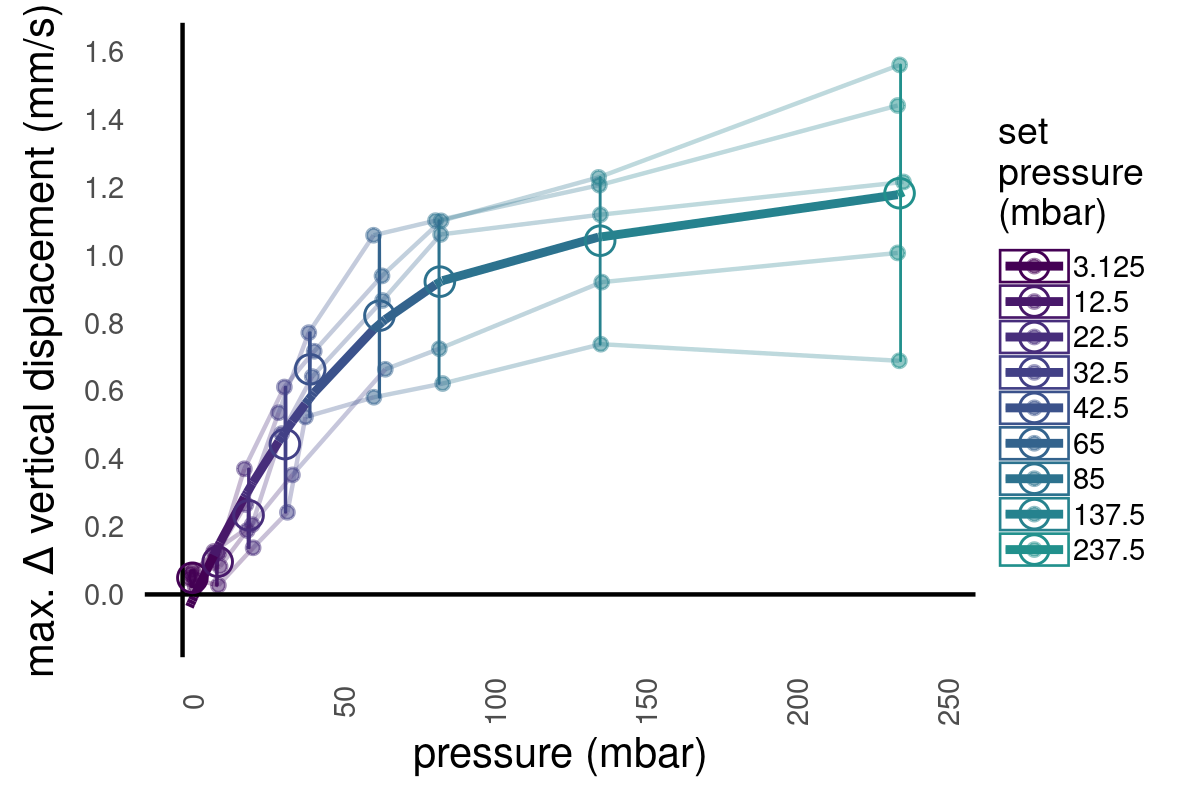

Luis A. Bezares-Calderón
Swimming speed increases, trajectories straighten
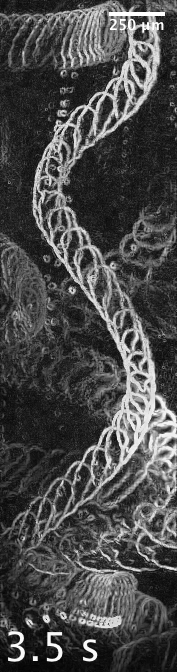 ctr
ctr
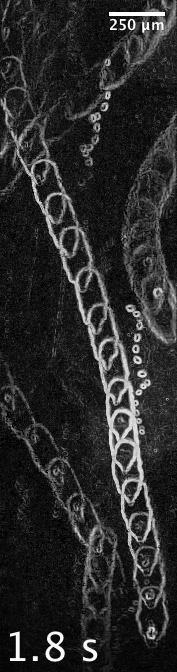 pressure
pressure
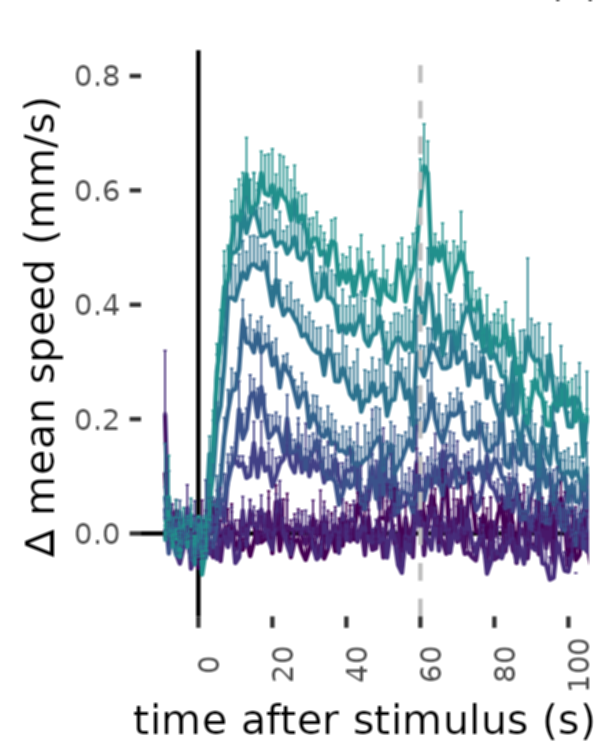

Luis A. Bezares-Calderón
Ciliary beating increases under pressure
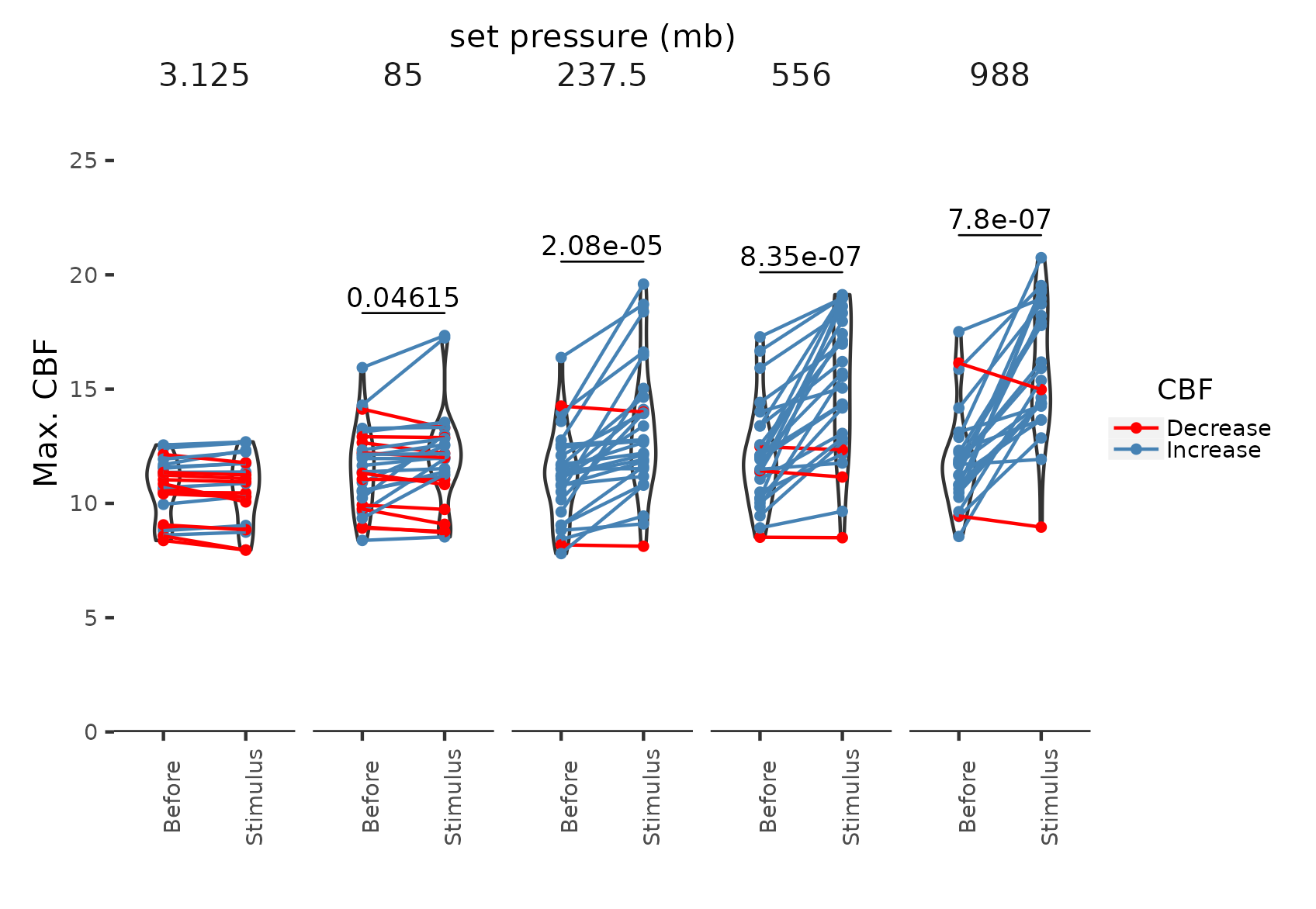

Luis A. Bezares-Calderón
Pressure is sensed by photoreceptors with ramified cilia
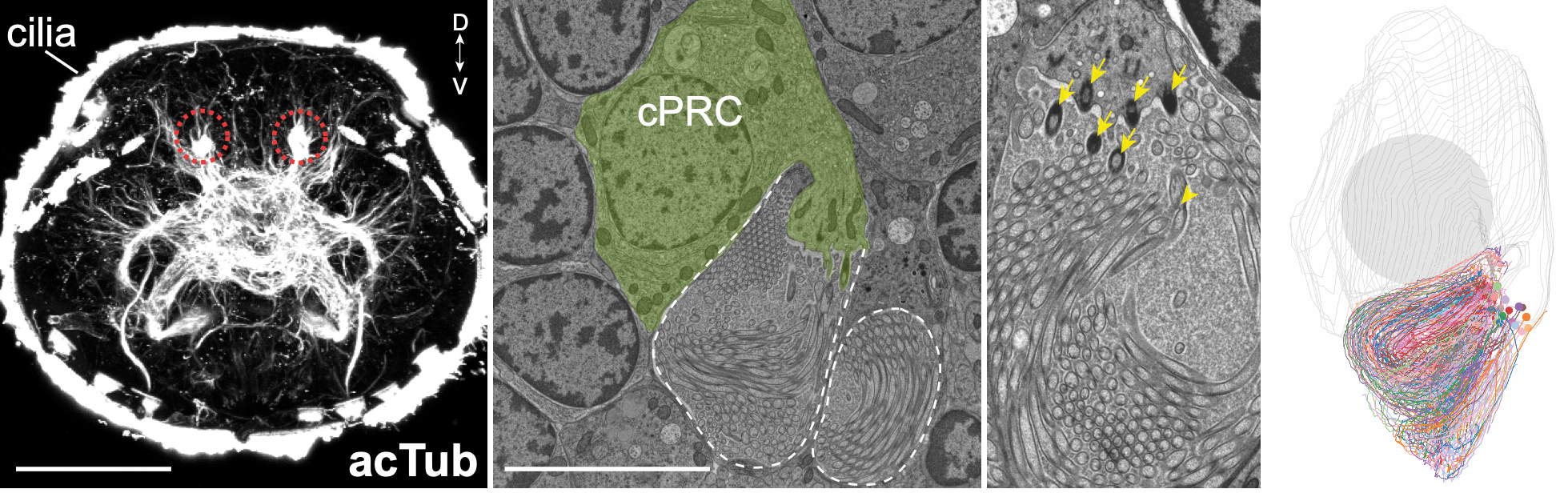 cPRC - ciliated Photoreceptor Cells
cPRC - ciliated Photoreceptor Cells
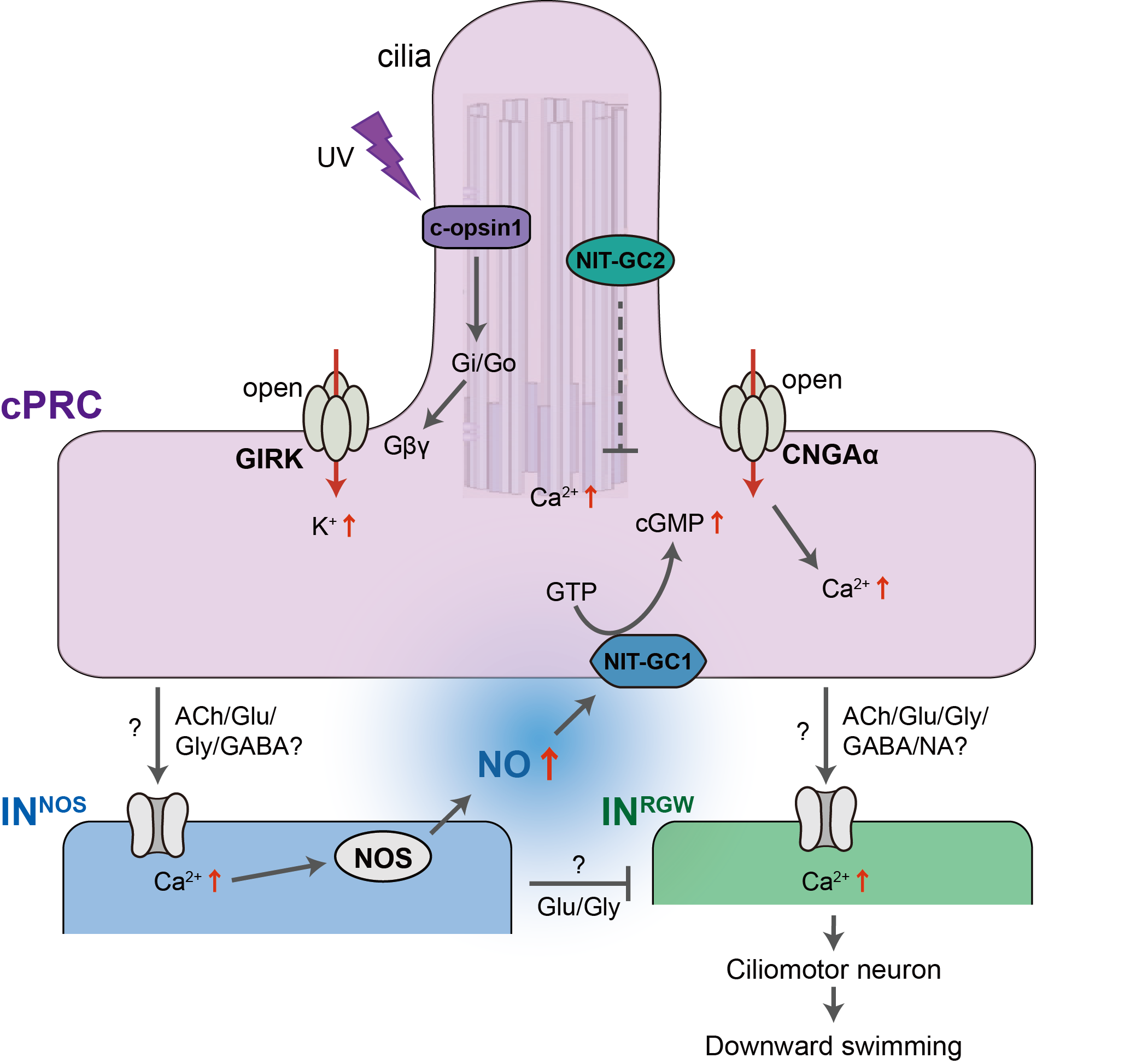
Circuitry of ciliary photoreceptors
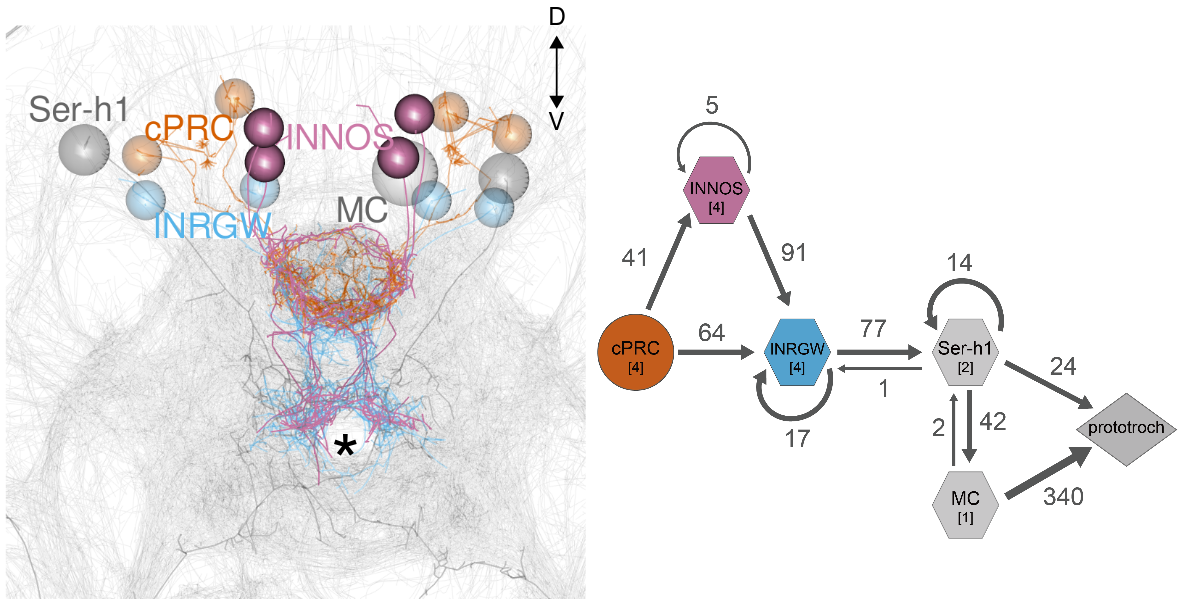
Circuitry of ciliary photoreceptors
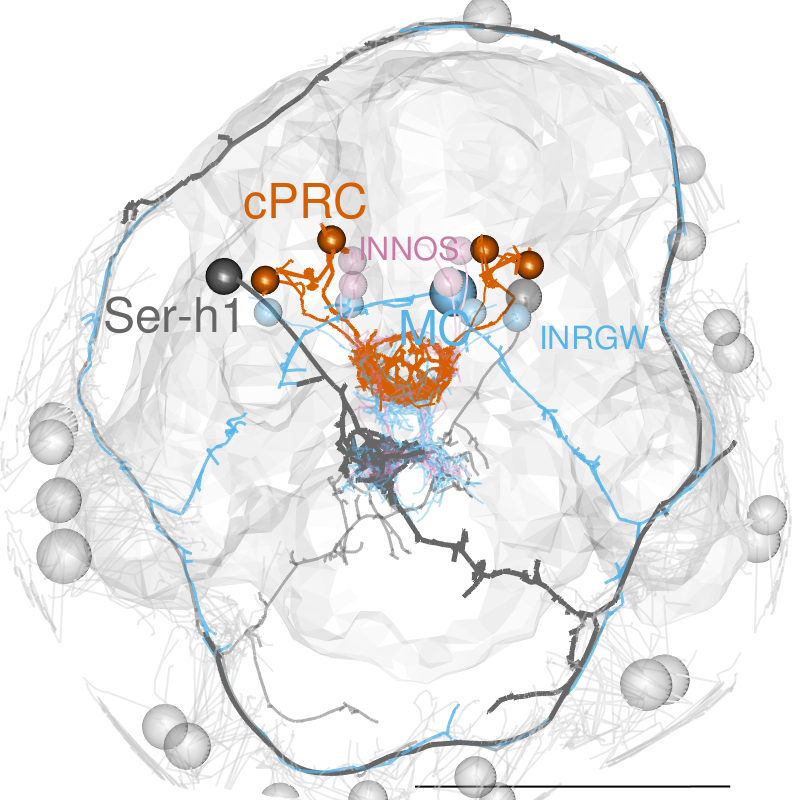
Serotonergic neurons to activate cilia
Ser-h1 neurons, EM reconstruction
Mechanisms of barotaxis
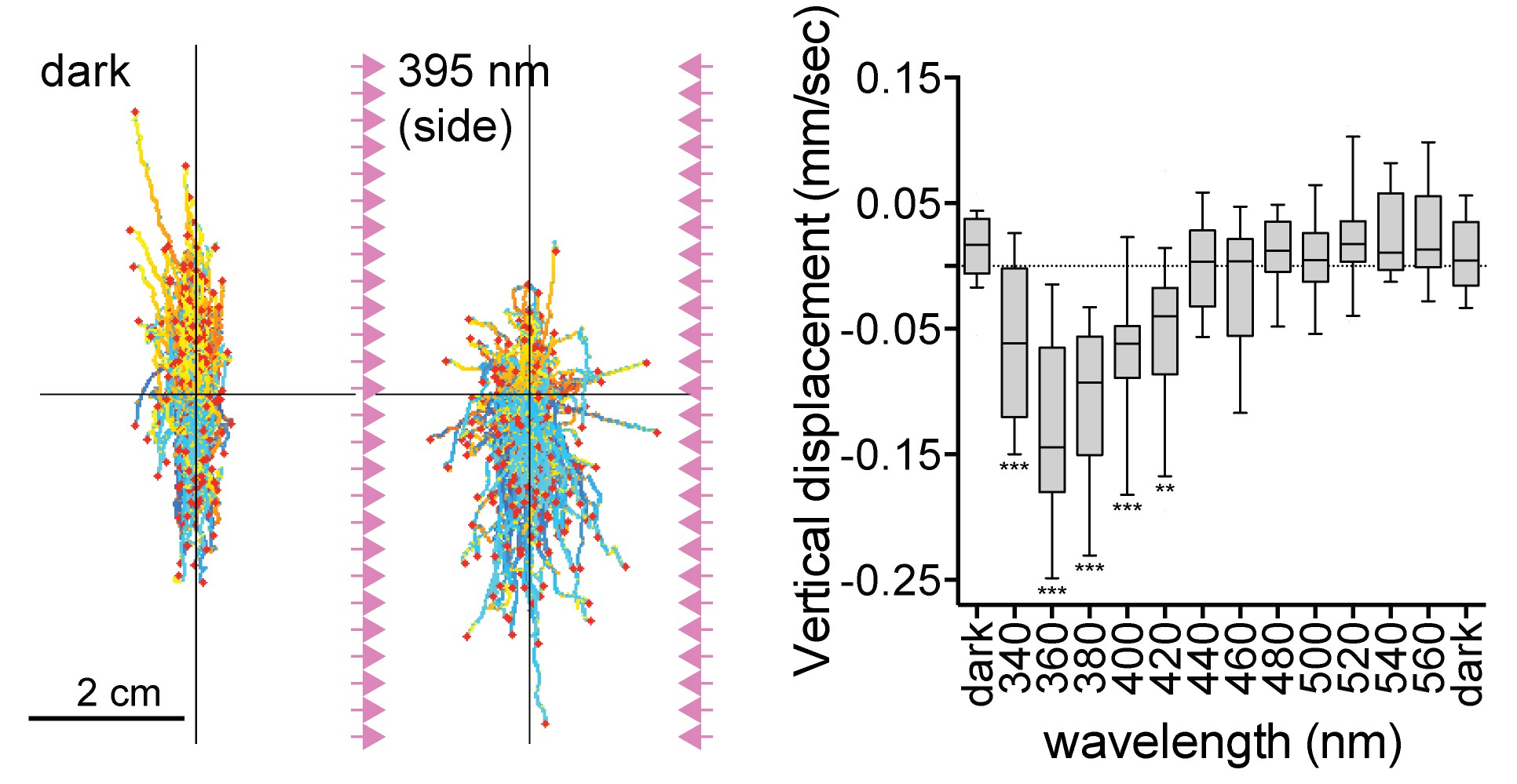
UV-responding brain ciliary photoreceptors (cPRCs)

UV response in Platynereis larvae

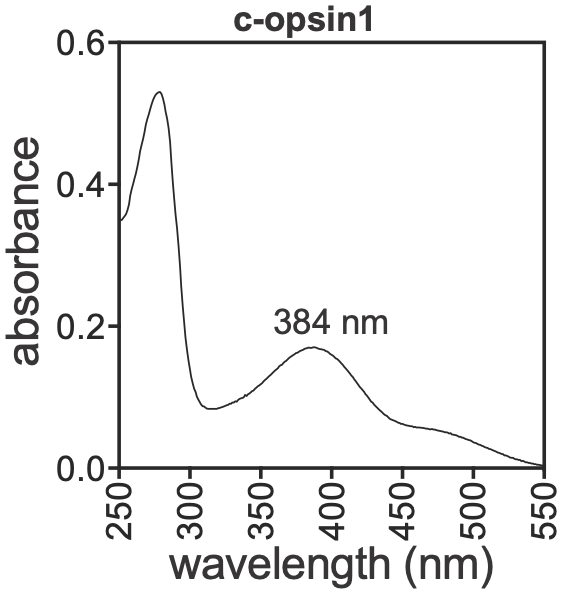
Mediated by a UV-absorbing c-opsin1 photopigment
No UV avoidance in c-opsin1 knockouts
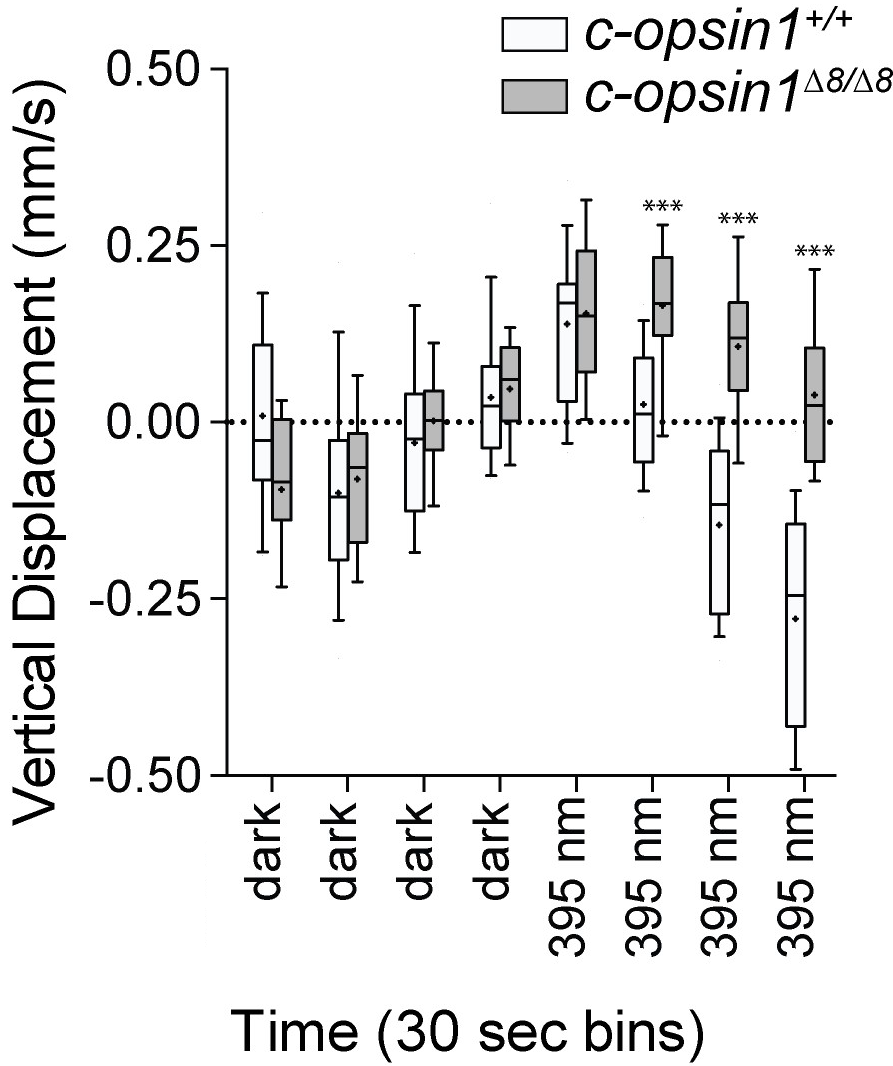
Strong c-opsin1-dependent cPRC activation by UV light
Kei Jokura and Verasztó, Gühmann et al. (2018)
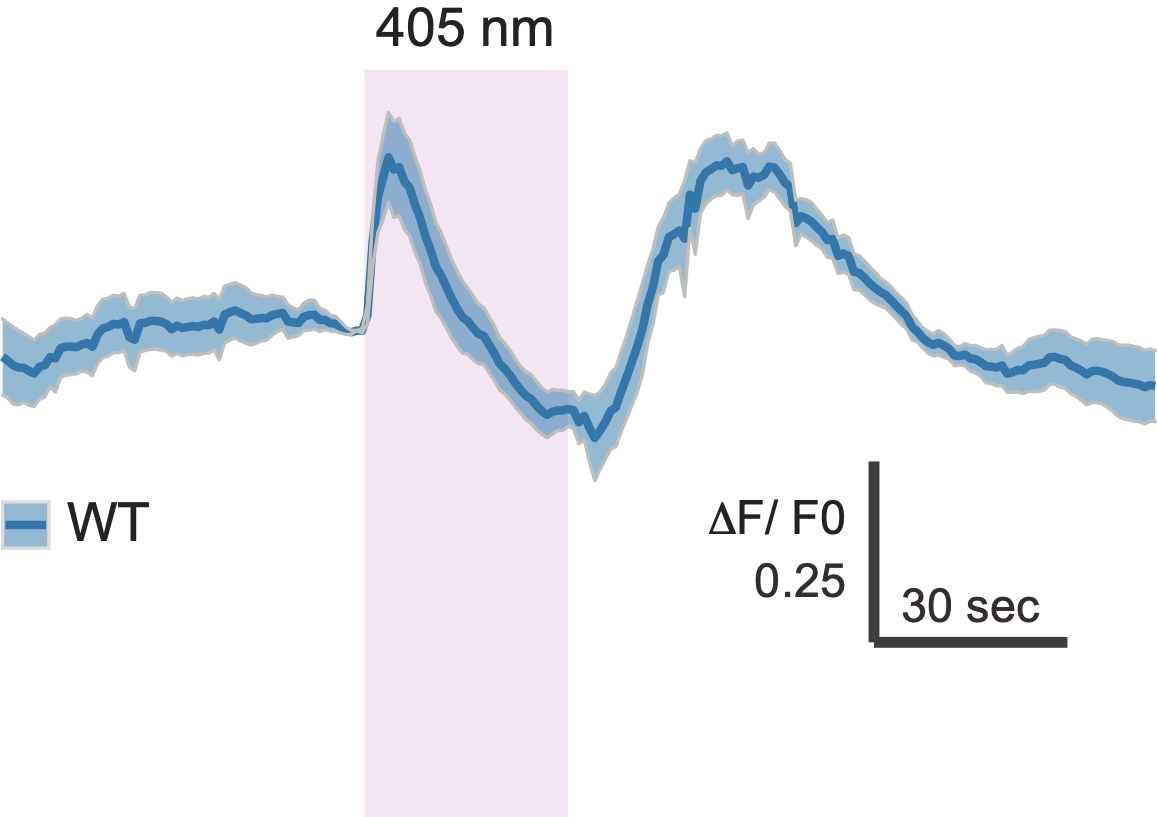
Nitric-oxyde synthase in postsynaptic interneurons
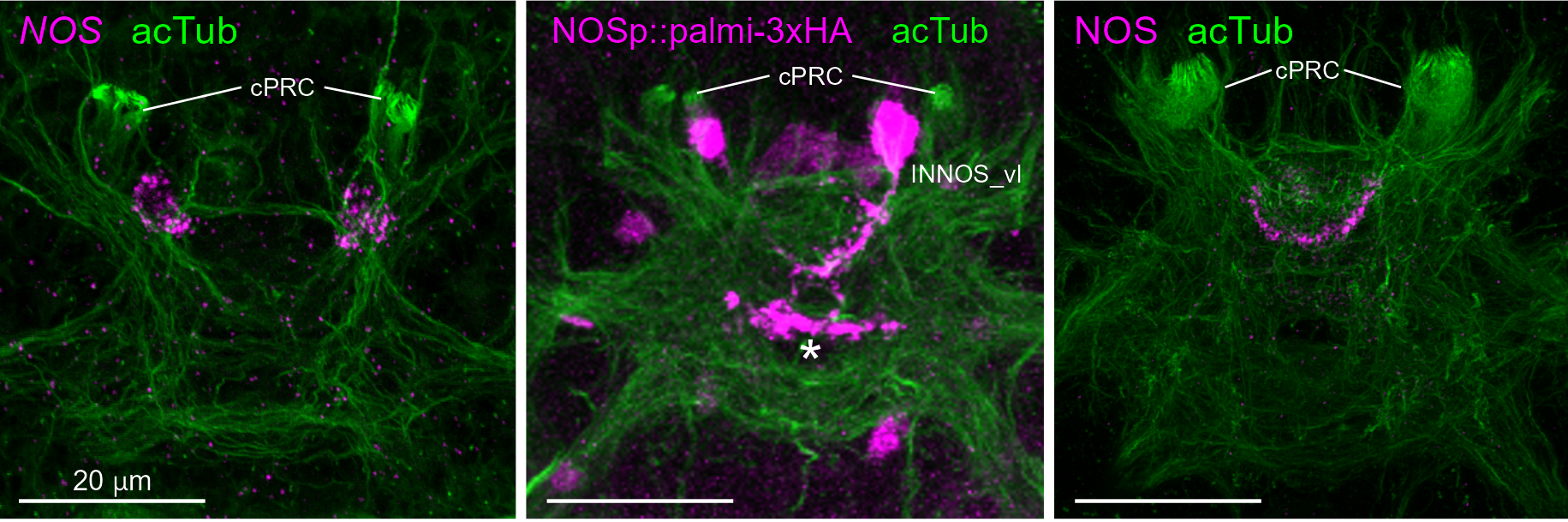
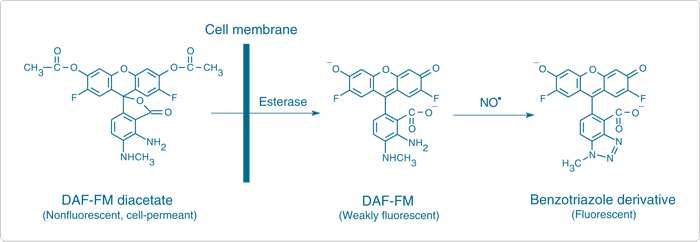
NO is produced in the neuropil after UV stimulation
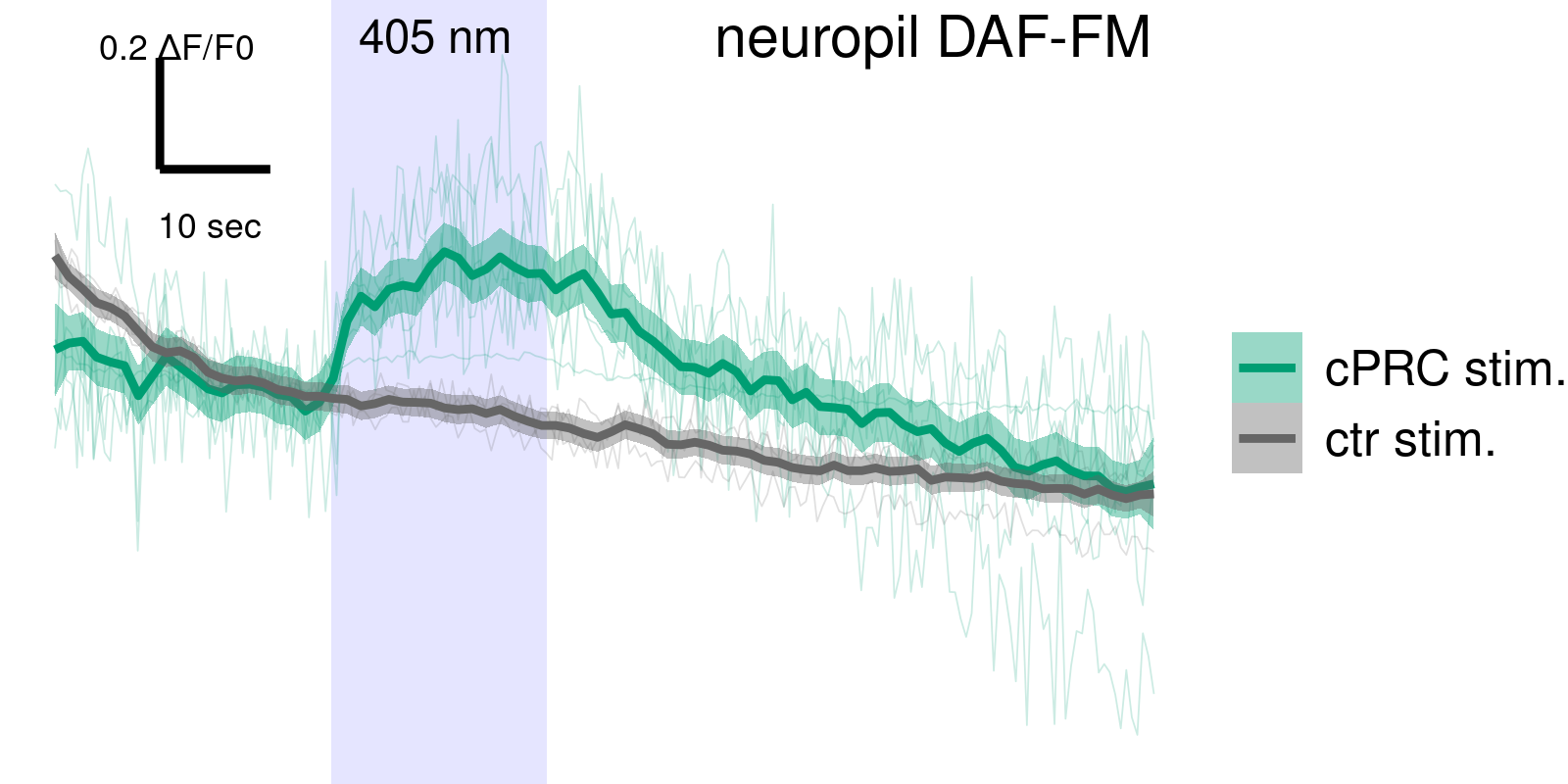
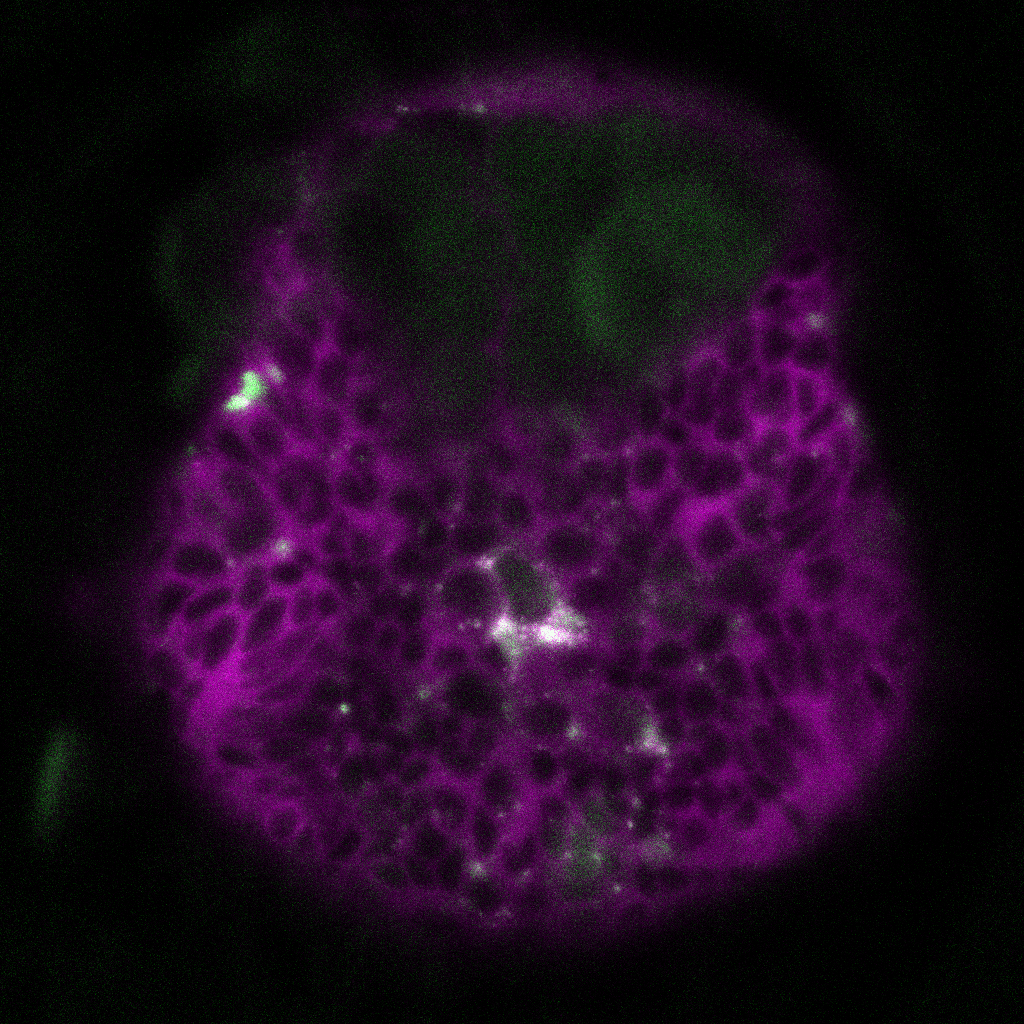
NOS mutants show defective UV avoidance
![]()
Kei Jokura
NOS mutants have altered cPRC response
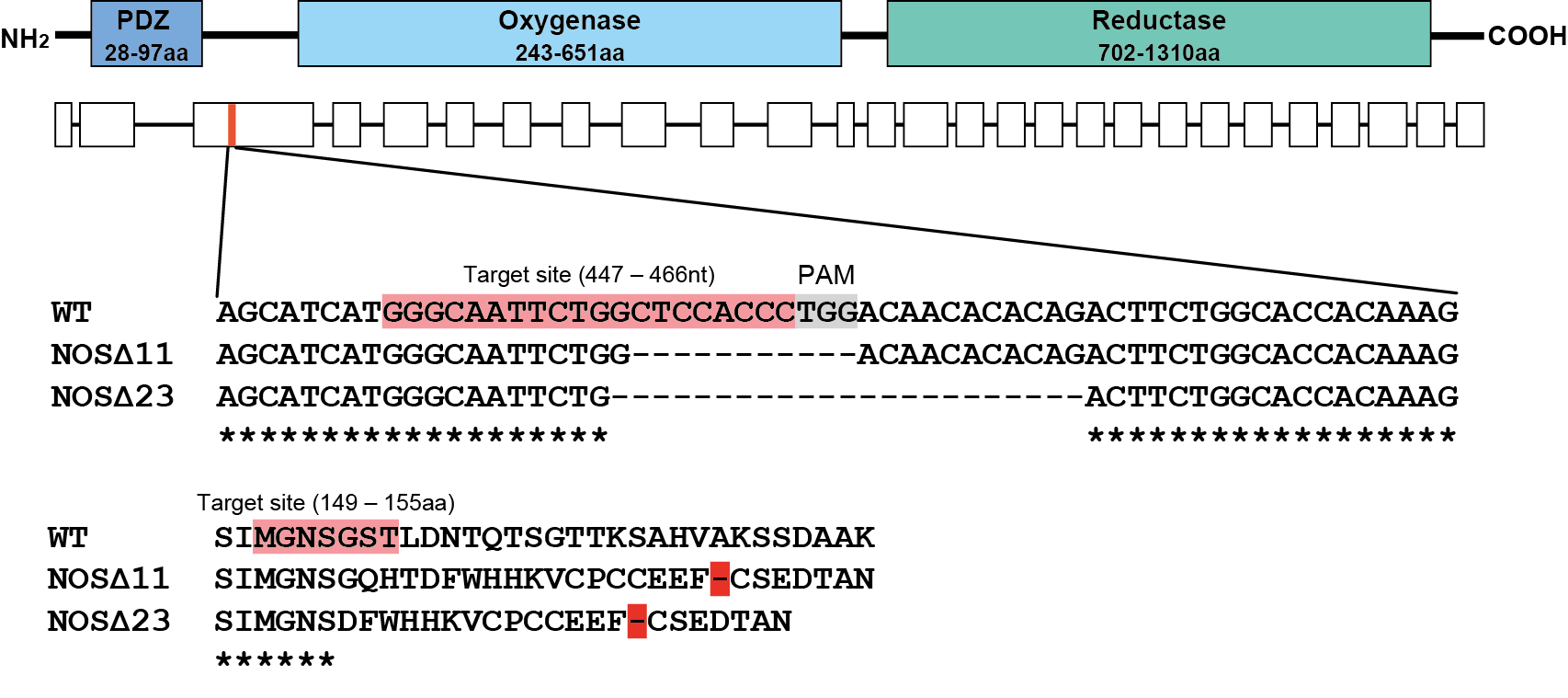
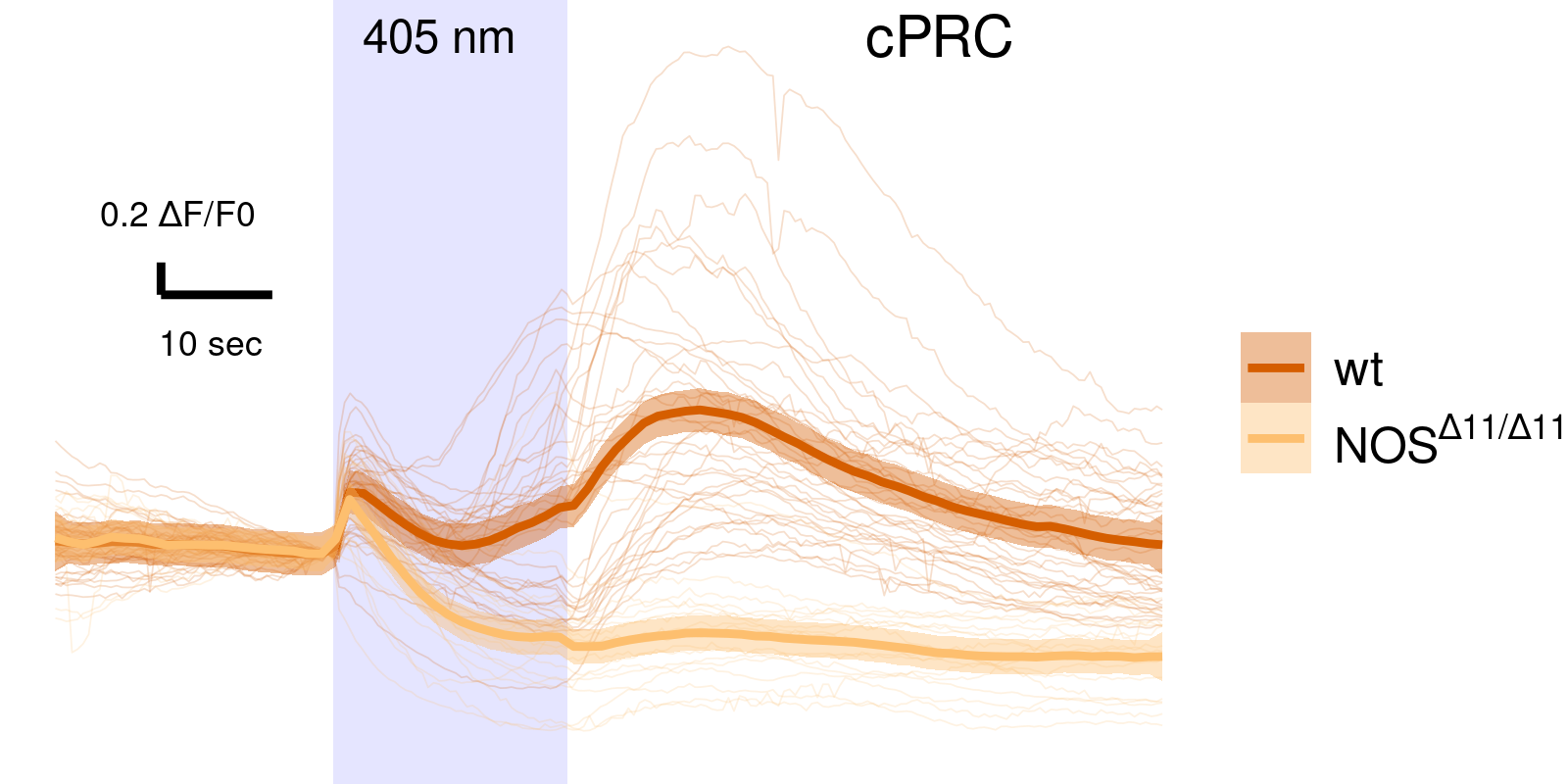
Nobuo Ueda, Kei Jokura
Mathematical modelling of the circuit
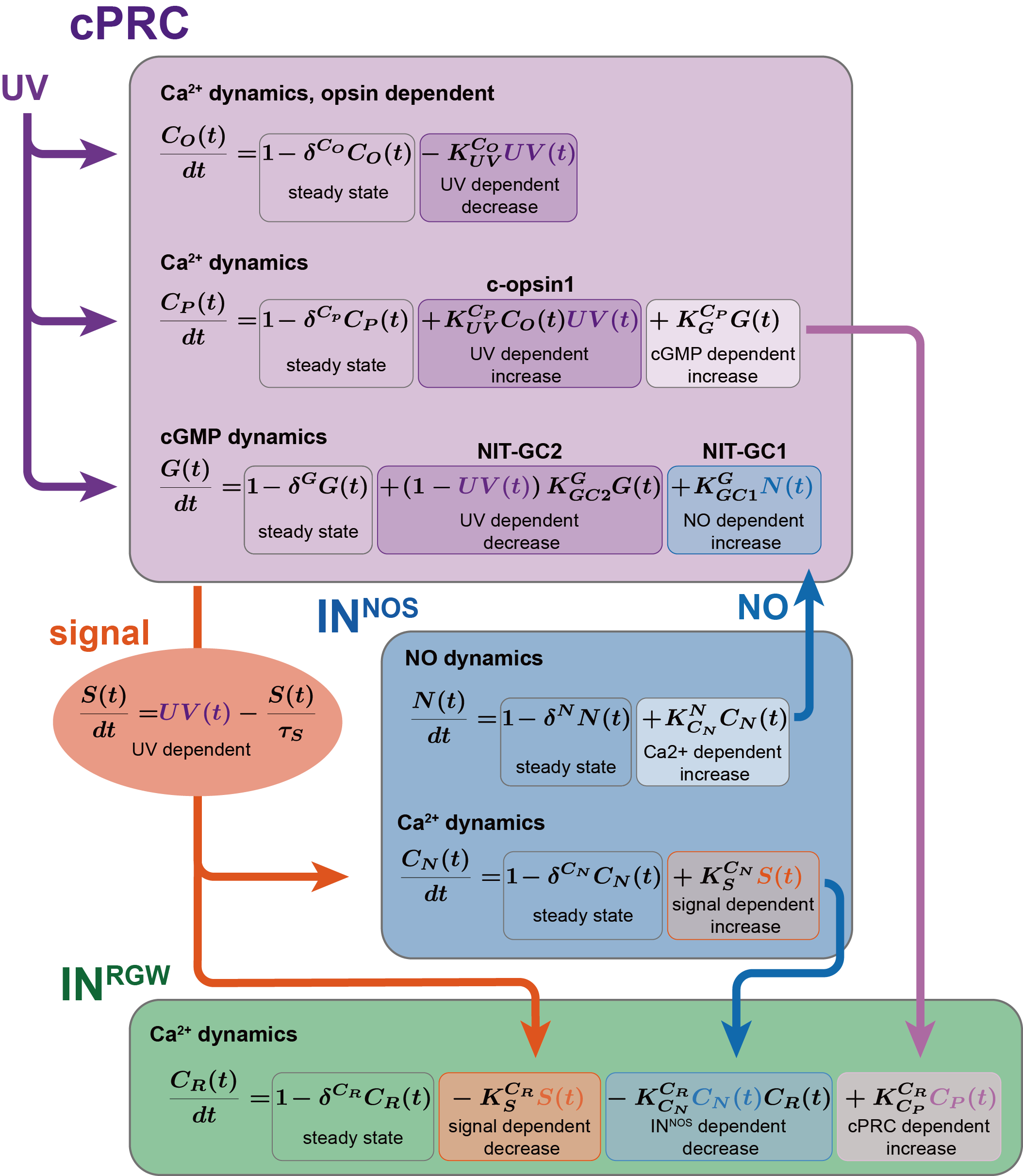
with Piotr Slowinski and Kyle Wedgewood, LSI Exeter
Integration and memory of UV exposure
What is the representation?
Principle 9: learning occurs at the lowest level to enable a causal influence on behaviour
Up or down?

 ‘front-wheel drive’ head cilia fast
‘front-wheel drive’ head cilia fast
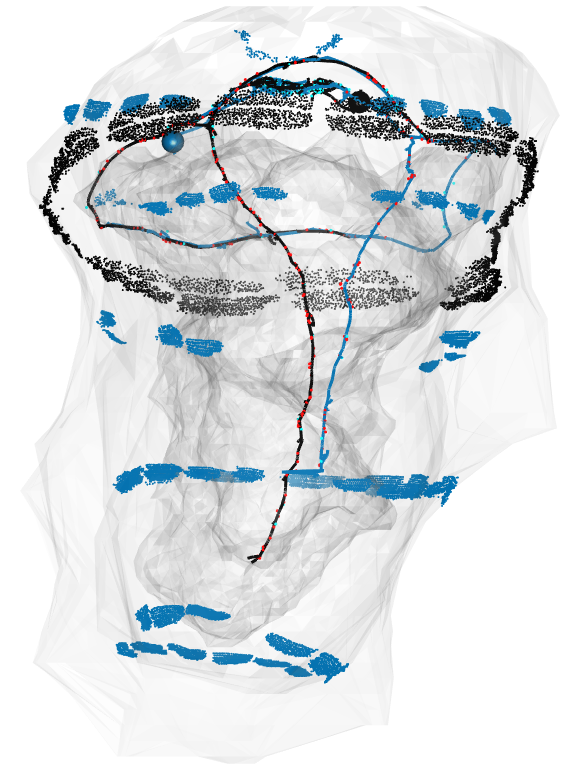 ‘rear-wheel drive’ head cilia slow
‘rear-wheel drive’ head cilia slow
Acknowledgements
- Emelie Brodrick
- Cyrielle Kaltenrieder
- Réza Shahidi
- Milena Marinkovic
- Daniel Thiel
- Sanja Jasek
- Cameron Hird
- Rebecca Turner
- Luis A. Bezares-Calderón
- Kei Jokura
- Luis Yanez Guerra
- Alexandra Kerbl


Former lab members
- Albina Asadulina
- James Beard
- Markus Conzelmann
- Nadine Randel
- Philipp Bauknecht
- Martin Gühmann
- Cristina Pineiro-Lopez
- Nobuo Ueda
- Aurora Panzera
- Csaba Verasztó
- Elizabeth Williams